

Raktamokshana
Sushruta, ‘the father of surgery’ had quoted Raktamokshana. It is one of the five Panchakarma procedures. Rakta means blood and moksha is letting, and is used for removing impure blood from the body. According to Acharya Vagbhata and Sushrutha, Raktamokshana is one among the PANCHA SHODHANA. Raktamokshana derives its name from Rakta meaning ‘blood’ and mokshana meaning ‘liberation’. This treatment literally ‘releases’ impure blood from the system. The legendary surgeon Sushruta is said to have been a major votary of this therapy, and his school actually combines the two Vasti treatments, and lists Raktamokshana as the fifth main Panchakarma. Toxin build-up in the bloodstream is a major cause of diseases and this method involves careful extraction of toxins from the human body.
Types of Raktamokshana
Pracchan
Alabu (gourd)
Shring (horn)
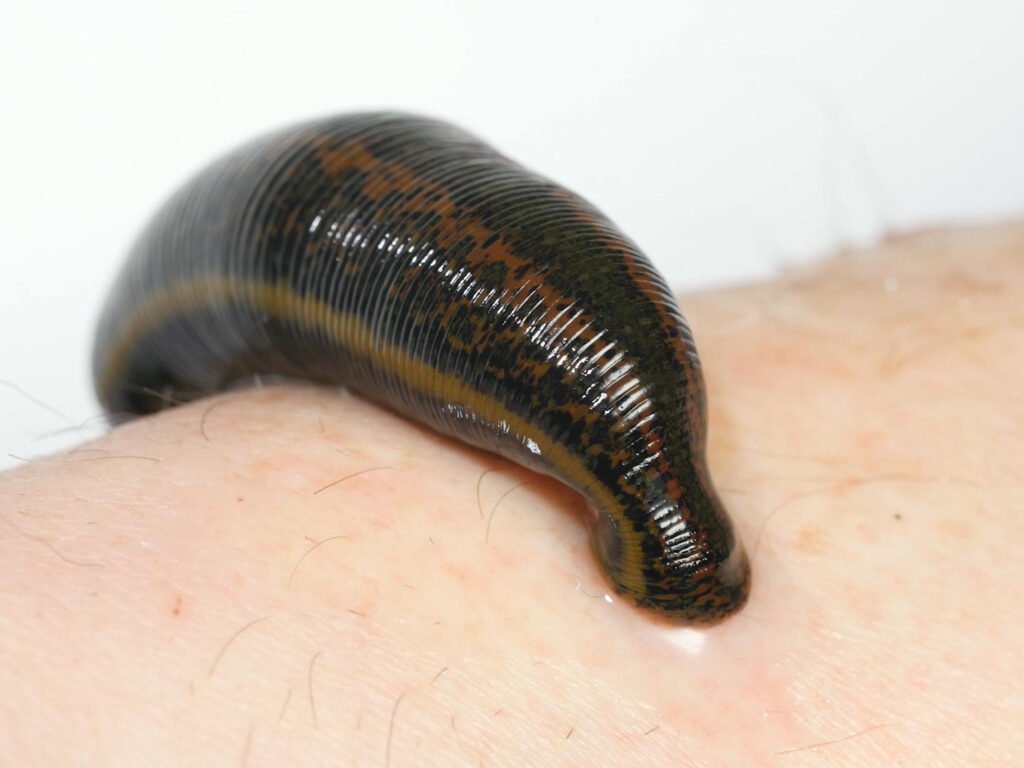
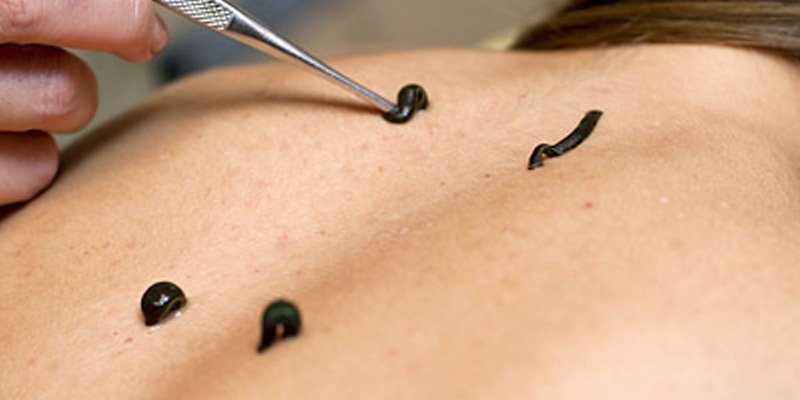
Jalauka (leeches)
Siravedha
प्रच्छानं पिण्डिते वा स्यात् अवगाढे जलौकसः
त्वक्स्ये अलाबुघटीश्रिङ्गम् शिरैवव्यापकेअसृजि
वातादिधाम वाँ श्रृङ्गजलोंकोलाबुभिः क्रमात् ॥ -(Ah. Su 26/54-55)
• Prachanna – Localized.
• Jaluka- Deep seated.
• Alabu, Shringa- Localized in the skin area.
• Siravedhana- Entire body.
Pracchan- Multiple incisions are made with a Scalp blade, vertically & parallel to the course of local blood vessels at the desired site.
Alabu- Alabu (through pitcher guard) Medium-sized selected pitcher is opened at the top to remove pulp and seed and dried under the sun till it is hard Affected part is cleaned with an antiseptic solution, and multiple vertical incisions are made over the site. An ignited wick is kept straight over the area and closed with the pitcher guard, the fire extinguishers creating the vacuum inside the pitcher which drains out the blood which gets collected at the margins of the pitcher
Shring- Shrunga (cow’s horn) Selected cow’s hom is collected which is open at both ends. Superficial multiple small incisions are made over the affected area which is cleaned properly with an antiseptic solution. The larger open end is kept over the incised area and blood is sucked through the other end.
Jalauka- Types, method of application Method of application of leech: Selected leeches are collected, to bite the affected area which is washed properly with an antiseptic solution. Once they start sucking the blood, it is covered with a moist cloth. Once it completes sucking the vitiated blood, they leave the site to fall off it. Then the area is rubbed with turmeric powder which helps to stop the bleeding.
Siravyadha – Siravyadha is done with a sharp instrument (needle, etc.) and as such, it is a more severe form of blood-letting.
